ABSTRACT
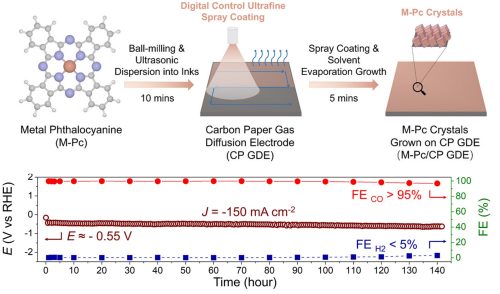
A research group from WPI-AIMR/Graduate School of Environmental Studies/International Synchrotron Radiation Innovation Smart Center (SRIS) at Tohoku University, RIES at Hokkaido University, and AZUL Energy Inc. has established a method for fabricating electrodes for CO2 electrolysis. This is achieved by directly crystallizing cobalt phthalocyanine (CoPc), a type of inexpensive pigment and metal complex, onto a gas diffusion electrode, simplifying the overall process. The team also developed a technique to convert CO2 into CO&madash;an essential precursor for synthetic fuels&mdash under high-speed electrolysis conditions of over 1 A/cm2 with more than 90% efficiency. Moreover, they demonstrated durability exceeding 140 hours.
The CO2 electrolysis technology developed in this study enables a low-cost and highly efficient process for synthesizing CO, a key intermediate for synthetic fuels, using inexpensive pigment catalysts. This breakthrough is expected to contribute to solving challenges as a next-generation CO2 Capture and Utilization (CCU) technology.
Information of the paper
| Title | Surface Charge Transfer Enhanced Cobalt-Phthalocyanine Crystals for Efficient CO2-to-CO Electroreduction with Large Current Density Exceeding 1000 mA cm-2. |
| Authors | Tengyi Liu*, Di Zhang*, Yutaro Hirai, Koju Ito, Kosuke Ishibashi, Naoto Todoroki, Yasutaka Matsuo, Jun Yoshida, Shimpei Ono, Hao Li*, Hiroshi Yabu* |
| Journal | Advanced Science |
| Publication | April 4, 2025 |
| DOI | 10.1002/advs.202501459 |
| URL | https://advanced.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/advs.202501459 |
Please refer to the following website of Hokkaido University
Laboratory of Nanostructured Functional Materials